20220427-FileProvider学习笔记
本文主要摘要FileProvider的关键知识点和记录我的学习思路及验证结论,可以帮助读者比较全面的认识FileProvider。如读者尚未了解何为FileProvider,请阅读安卓官网的FileProvider参考和分享文件指南。
FileProvider的基本面
最小原型
FileProvider是特殊的ContentProvider,目标是在为保护隐私和数据安全而加强应用沙箱机制的同时,支持在应用间共享文件。关于ContentProvider的方方面面,请参考安卓官网的相关参考和指南。FileProvider共享的客体是单个文件,如果需要共享整个目录,请参考DocumentsProvider。
下图是FileProvider的工作模型:
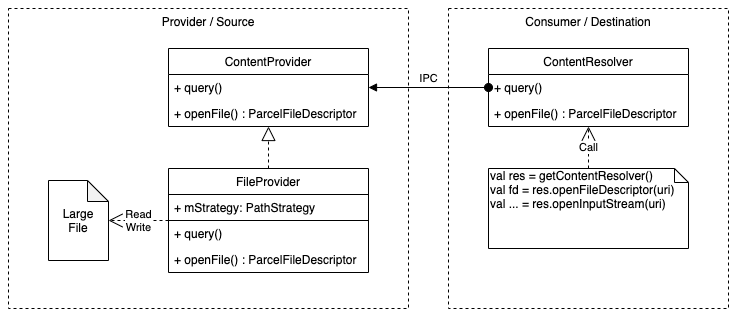
下面假设存在源应用沙箱的files/some/internal/path/1.dat文件共享给目标应用,展示双方应用要达成目标的最小代码原型。首先是源应用:
// build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:+'
}
<!-- AndroidManifest.xml -->
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.provider">
<provider android:name="androidx.core.content.FileProvider"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.fileprovider"
android:exported="false"
android:grantUriPermissions="true">
<meta-data android:name="android.support.FILE_PROVIDER_PATHS"
android:resource="@xml/paths"/>
</provider>
</manifest>
<!-- res/xml/paths.xml -->
<paths xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<files-path name="name-example" path="some/internal/path" />
<!-- write extra paths rules here -->
</paths>
然后是目标应用:
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.provider.fileprovider/name-example/1.dat");
InputStream istream = getContentResolver().openInputStream(uri);
// ParcelFileDesciptor fd = getContentResolver().openFileDescriptor(uri, ...);
// read from istream or operate fd
// ...
以上就是让FileProvider能够成功运行的核心代码(最小原型)。如果要在正式的工程项目中使用FileProvider,还需要一些额外代码,但始终都不脱离上述核心代码。下面对一些基础要点展开介绍。
源应用各项配置的说明
android:name
如上文所说,FileProvider是ContentProvider的子类,AndroidManifest.xml的配置标签也是<provider/>,所以FileProvider也属于四大组件。跟所有四大组件一样,android:name就是FileProvider的实现者类名。
FileProvider的name默认指定androidx.core.content.FileProvider就够了,但这并不是严格要求。某些应用场景会需要提供androidx.core.content.FileProvider的子类,关于这个话题将在后面的章节展开介绍。
androidx.core.content.FileProvider是androidx.core:core:+提供的,可以直接添加androidx.core:core:+依赖、或通过androidx.appcompat:appcompat:+间接依赖。
android:authorities
参考<provider>的指南,FileProvider没有特殊要求。
android:export
FileProvider要求本字段必须配置false,然后针对uri授予临时权限。配置true会导致编译期报错。本字段的更多说明请参考<provider>的指南。关于权限的问题,参考权限管理一节。
<paths/>
本配置是FileProvider提供的安全策略,可以隐藏沙箱目录的一些具体细节。文件必须位于<paths/>标签下配置的目录下,才可以被FileProvider共享。
<paths/>标签下可以插入多条配置。对files目录下的文件需要用<files-path/>标签配置策略,如上文的示例代码。<paths/>标签下还支持配置缓存目录、外存目录、等其他目录,详细说明请参考FileProvider参考。
<paths/>的配置会影响文件的uri,如上文示例代码那样。详细说明参考后续章节uri的默认规则。
怎么实现端对端的uri传递
ContentProvider的uri通常由源应用定义。除非源应用和目标应用有过事先约定,否则目标应用是很难自己生成正确uri的。FileProvider封装的PathStrategy,并基于PathStrategy提供了一套生成uri的规则。
uri的默认规则
在源应用中,uri需要通过FileProvider.getUriFromFile(..., file)获取,方法内部会遍历PathStrategy的所有策略,根据匹配的策略把文件路径映射为uri。相对的,在目标应用调用FileProvider读写文件的时候,FileProvider会根据相同的PathStrategy反向把uri映射为文件路径。
在上文的示例代码中,文件路径files/some/internal/path/1.dat命中了规则<files-path name="name-example" path="some/internal/path" />,其中files对应<files-path/>、some/internal/path对应path="..."。FileProvider会把files/some/internal/path部分替换为name="..."的值,加上FileProvider的authority,就得到了content://com.example.provider.fileprovider/name-example/1.dat。
类似的,如果上文示例代码存在如下配置:
<!-- res/xml/paths.xml -->
<paths xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<files-path name="name-example" path="some/internal/path" />
<files-path name="another-example" path="another/internal/path" />
</paths>
假设要共享的文件为files/another/internal/path/some/image/2.png,则映射uri的结果是content://com.example.provider.fileprovider/another-example/some/image/2.png。
基于FileProvider的映射规则,只要①FileProvider事先完成了对uri的授权,且②目标应用预先知道了某个文件的相对路径,那么从技术上来说,目标应用可以不需要源应用告诉,就能自己根据源应用的<paths/>配置生成正确的uri。在实际项目中仍然需要应用间通过IPC途径传递uri,正是因为上述①②两点很难满足、且不应轻易满足。
通过Intent传递uri
Intent是常用的进程间通信载体。通过Intent传递uri的最小原型如下:
Uri uri = ...;
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setData(uri);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION);
// send the intent
uri一定要通过setData(在APILEVEL ∈ [16, 22]的设备上需要使用setClipData()方法)设置;- 一定要通过
setFlags设置uri的读写权限;
如果上述两点没有满足,目标应用在使用uri的时候会得到一个java.lang.SecurityException: Permission Denial异常。
上面的Intent可以通过多种方式发送到目标应用:
Context.startActivity(intent):如调用另一个应用打开沙箱内的一个文档;Activity.setResult(intent):如调用一个文件选择器返回一个文档;Context.startService(intent);- Android定义的其他其他
Intent发送的手段;
上述方案除了uri授权的有效期略有不同以外,本质上是一样的,可依据具体应用场景选用。关于uri授权有效期的问题,会在权限管理一节介绍。
通过Intent以外的IPC方式传递uri
典型的方法是Binder。例如定义如下aidl:
interface IDocumentRepositoty {
Uri requestDocument(String myPackageName, String documentName);
}
关于Binder和aidl的使用方法,可参考Android 接口定义语言 (AIDL),本文不做展开。
在源应用返回uri之前,一定要通过Context.grantUriPermissions()方法设置uri的读写权限,否则目标应用在使用uri时会得到一个java.lang.SecurityException: Permission Denial异常。
public class RepositoryImpl implements IDocumentRepositoty.Stub {
Context context = ...;
public Uri requestDocument(String toPackageName, String documentName) {
Uri uri = ...;
context.grantUriPermissions(toPackageName, uri, Intent.FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION);
return uri;
}
}
权限管理一节会对Context.grantUriPermissions()做更多介绍。
FileProvider的展开
权限管理
基本点
权限管理的目标是控制所有uri的读写权限,权限可以是只读、只写、可读可写。所有uri在通过授权之前,默认是不能被读写的,否则会收到java.lang.SecurityException: Permission Denial异常。对只读uri做写操作、或对只写uri做读操作,都会收到异常。
授权的粒度是uri×目标应用包名。对相同目标应用,不同的uri要分别授权;对相同的uri、不同的目标应用也要分别授权。基于这样的粒度,所以不用担心预期之外的应用强行读写uri,也不用担心授权的目标应用随意生成uri枚举源应用内的文件。
在通过Intent传递uri的时候,如果通过Intent.setFlags()设置了读或写权限,那么有且只有收到Intent的应用能获得授权。收到Intent后,该应用的所有代码都能获得授权,跟收到Intent的是Activity、Service、或其他组件无关。
如果没有通过Intent.setFlags()授权,则需要通过Context.grantUriPermissions(toPackage, uri, flags)授权,其中参数toPackage是目标应用的包名。
授权的有效期
uri的授权都是临时授权。根据授权方式不同,授权的有效期和过期规则略有差异。一旦授权过期或取消了,就需要源应用重新授权。
通过Intent.setFlags()授权,根据接收Intent的组件不同,授权有效期的判断依据有差异:
- 如果
Intent接收组件为Activity,则其所在栈的所有Activity执行onDestroy之后,授权就过期了; - 如果
Intent的接收组件为Service,则该Service执行onDestroy之后,授权就过期了;
通过Context.grantUriPermissions(toPackage, ...)授权,当toPackage指向的应用的所有进程都结束后,授权就过期了。
除了上述由Android管理的过期策略,应用还可以调用Context.revokeUriPermission(uri, ...)主动收回授权。
限制可共享文件的范围
通过FileProvider共享的文件,都必须位于<paths/>配置包含的目录下;分享一个不在这些目录下的文件会在调用getUriFromFile的时候收到一个异常。为叙述方便,下文将这些符合<paths/>配置的文件简称为“paths集合”。
在上文最小原型示例中,FileProvider的android:grantUriPermissions字段配置为true,其效果是所有属于paths集合的文件都可以共享。如果android:grantUriPermissions配置为false,则需要配置<grant-uri-permission/>定义一个子集(下文简称为“grant集合”)。paths集合和grant集合的交集才是可以共享的文件集合。更多说明请参考官网指南:android:grantUriPermissions和<grant-uri-permission/>。
多个FileProvider并存
Android允许定义多个FileProvider,应用构建的时候AGP似乎并不会校验这些FileProvider配置是否有重复或冲突,但是在运行时可能会得到预期之外的结果。
这里列出一些典型的情况(假设配置了两个FileProvider,且两者的<paths/>配置不同):
- 如果
android:name相同、android:authorities也相同:只有写在前面的FileProvider是有效的,后面的FileProvider的<paths/>配置对getUriForFile()不可见;源应用调用getUriForFile()获取第二个FileProvider的uri的时候,会得到java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Failed to find configured root异常。 - 如果
android:name相同、android:authorities不同:源应用在调用getUriForFile()的时候能得到正确的uri;目标应用通过uri访问文件的时候,只能解析写在前面的FileProvider的uri,解析后面的FileProvider的uri时会得到java.lang.SecurityException: The authority does not match异常。 - 如果
android:name不同(如继承自FileProvider的子类)、android:authorities相同:源应用会得到跟第一种情况相同的结果。 - 如果
android:name不同、android:authorities也不同:源应用调用getUriForFile()时传入正确的authority就能得到正确的uri;目标应用也可以成功的访问uri指向的文件。
基于上面的情况,项目中每个模块在提供FileProvider的时候,比较好的做法是:
android:name用从FileProvider继承的子类类名;android:authorities使用不容易跟别人重复的值;
自定义Uri格式
FileProvider可以被继承,Android允许子类重载FileProvider的默认行为。这里介绍如何通过重载FileProvider来自定义uri格式。
下面演示如何把形如content://${authority}/${name}/${relativePath}的uri按照content://${authority}/${md5FromFilePath}的格式加密,如content://com.example.fileprovider/c2681e80365f7f9f041875cbd25e4c20。如果源应用想对目标应用完全隐藏其文件在沙箱中的路径信息,可以考虑类似方案。
首先继承FileProvider并重载所有openFile():
public class MyFileProvider extends FileProvider {
static Map<Uri, Uri> mappedUris = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); // alternative to original
public static Uri getUriForFile(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull String authority, @NonNull File file) {
Uri original = FileProvider.getUriForFile(context, authority, file);
String md5 = getMD5(original.getPath());
Uri alternative = Uri.parse(original.getScheme() + "://" + original.getAuthority() + "/" + md5);
synchronized (mappedUris) {
for (Entry<Uri, Uri> entry : mappedUris.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().equals(original)) {
return entry.getKey();
}
}
mappedUris.put(alternative, original);
}
return alternative;
}
@Override
public ParcelFileDescriptor openFile(@NonNull Uri uri, @NonNull String mode) throws FileNotFoundException {
Uri originalUri = mappedUris.get(uri);
if (originalUri == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}
return super.openFile(originalUri, mode);
}
//...
}
然后使用加密后的uri:
// Uri normalUri = FileProvider.getUriForFile(context, authority, sourceFile);
Uri hashedUri = MyFileProvider.getUriForFile(context, authority, sourceFile);
intent.setData(hashedUri); // 因为重载了openFile(),所以传递normalUri会让目标应用收到一个FileNotFoundException
目标应用不需要做任何修改。
FileProvider的深入
FileProvider文件共享的本质
假设目标应用通过ContentResolver#openInputStream()方法访问文件:
public final @Nullable InputStream openInputStream(@NonNull Uri uri) throws FileNotFoundException {
String scheme = uri.getScheme();
if (SCHEME_ANDROID_RESOURCE.equals(scheme)) {
//...
} else if (SCHEME_FILE.equals(scheme)) {
//...
} else {
AssetFileDescriptor fd = openAssetFileDescriptor(uri, "r", null);
//...
}
}
跟随如上代码继续阅读,最终能调用到ContentProvider#openTypedAssetFile()方法:
public @Nullable AssetFileDescriptor openTypedAssetFile(@NonNull Uri uri, @NonNull String mimeTypeFilter, @Nullable Bundle opts) throws FileNotFoundException {
//...
return openAssetFile(uri, "r");
//...
}
ContentProvider#openAssetFile()方法:
1710 public @Nullable AssetFileDescriptor openAssetFile(@NonNull Uri uri, @NonNull String mode)
1711 throws FileNotFoundException {
1712 ParcelFileDescriptor fd = openFile(uri, mode);
1713 return fd != null ? new AssetFileDescriptor(fd, 0, -1) : null;
1714 }
FileProvider#openFile()方法:
public ParcelFileDescriptor openFile(@NonNull Uri uri, @NonNull String mode) throws FileNotFoundException {
// ContentProvider has already checked granted permissions
final File file = mStrategy.getFileForUri(uri);
final int fileMode = modeToMode(mode);
return ParcelFileDescriptor.open(file, fileMode);
}
最终收敛到ParcelFileDescriptor.open(file, fileMode)方法上。目标应用通过其他接口访问文件最终基本都收敛到此方法上。
根据上述分析,可以得到以下结论:
- 文件共享的本质不是跨进程传输文件字节流,而是跨进程传输FD;
- FD可以通过binder传输,且保障了FD跨进程可用;
FD跨进程传输
Linux的FD跟Windows的Handle本质上类似,都是对进程中一个指针数组的索引,这个指针数组的每个元素分别指向了一个内核态数据。
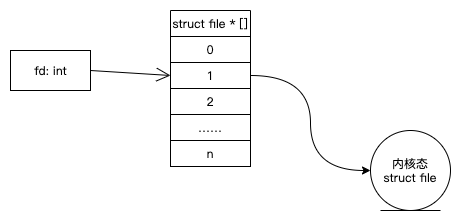
每个进程都有自己的指针数组,不同进程的指针数据一个各不相同,所以FD的值只有在进程内有意义,另一个进程的相同FD取值可能指向的完全是另一个对象,或根本没有指向任何对象(野指针或空指针)。所以直接跨进程传送FD的值是没有意义的。
可以推测binder可能对FD做了特殊处理。这一推测可以从binder.c的binder_transaction函数中(源码)找到证据:
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc, struct binder_thread *thread, struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply) {
//...
switch (fp->type) {
//...
case BINDER_TYPE_FD: {
int target_fd;
struct file *file;
//...
file = fget(fp->handle); // 1. 用源进程的FD获得file*
//...
security_binder_transfer_file(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk, file);
//...
target_fd = task_get_unused_fd_flags(target_proc, O_CLOEXEC); // 2. 在目标进程分配新的FD
//...
task_fd_install(target_proc, target_fd, file); // 3. 把file*赋值给新FD
//...
fp->handle = target_fd; // 4. 把新FD发给目标进程
} break;
//...
}
//...
}
binder通过上面代码中的4个关键步骤,在目标进程分配新的FD并让其指向内核的file对象。FD的跨进程传递的本质是file对象指针的跨进程传递。
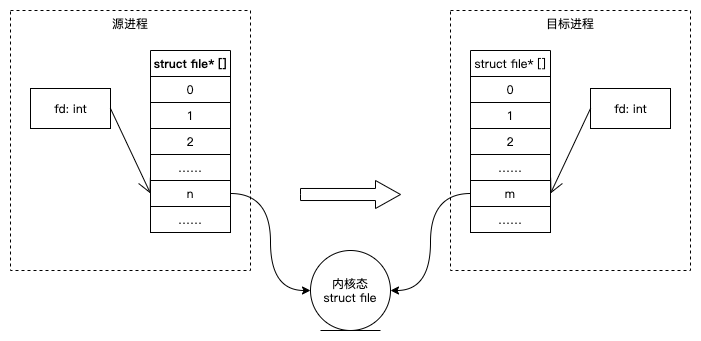
关于上述步骤的相关源码可参考:
- fget → __fget → fcheck_files参考
- task_get_unused_fd_flags → __alloc_fd → __set_open_fd
- task_fd_install → __fd_install
上述源码中还调用了security_binder_transfer_file函数,本质上是对selinux_binder_transfer_file函数的调用。该函数负责校验进程双方是否具有传递此FD的权限,更多介绍可参考罗升阳的《SEAndroid安全机制对Binder IPC的保护分析》,这里不做展开。
FileProvider以外的FD跨进程传递
既然FD是通过binder保障了跨进程传递,那么FileProvider就不是文件共享的唯一途径,其他基于binder的IPC方法应该也可以传递FD,例如:
- 通过
Intent调用四大组件,如Activity、Service、BroadcastReceiver; - 通过
FileProvider以外的ContentProvider; - 通过
aidl调用;
aidl调用
例如有如下aidl:
interface ISampleAidl {
void sendFile(in ParcelFileDescriptor fd);
ParcelFileDescriptor recvFile();
}
通过入参可以从主调进程把FD传递给被调进程;通过返回值可以从被调进程把FD传递给主调进程。除了直接在入参和返回值使用ParcelFileDescriptor,还可以通过其他Parcelable类型(如Bundle等)携带FD。
FileProvider以外的ContentProvider
例如在源应用做如下自定义Provider:
public class MyContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
@Nullable
@Override
public ParcelFileDescriptor openFile(@NonNull Uri uri, @NonNull String mode) throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = ...;
return ParcelFileDescriptor.open(file, ParcelFileDescriptor.MODE_READ_ONLY);
}
}
在目标应用有类似如下调用:
Uri uri = ...;
try (ParcelFileDescriptor fd = getContentResolver().openFileDescriptor(uri, "r")) {
readFromFD(fd);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
本质上FileProvider就是基于此模型而封装的库。
通过Intent调用四大组件
调用四大组件的方法有但不限于以下方法:
Context#startActivity(Intent)Context#startService(Intent)Context#sendBroadcast(Intent)
例如通过如下方法携带FD:
ParcelFileDescriptor fd = ...;
Intent intent = new Intent();
//...
intent.putExtra("file", fd);
startActivity(intent); // RuntimeException: Not allowed to write file descriptors here
意外的是,调用startActivity的时候发生了异常:
java.lang.RuntimeException: Not allowed to write file descriptors here
at android.os.Parcel.nativeWriteFileDescriptor(Native Method)
at android.os.Parcel.writeFileDescriptor(Parcel.java:809)
at android.os.ParcelFileDescriptor.writeToParcel(ParcelFileDescriptor.java:1057)
at android.os.Parcel.writeParcelable(Parcel.java:1801)
at android.os.Parcel.writeValue(Parcel.java:1707)
at android.os.Parcel.writeArrayMapInternal(Parcel.java:928)
at android.os.BaseBundle.writeToParcelInner(BaseBundle.java:1584)
at android.os.Bundle.writeToParcel(Bundle.java:1253)
at android.os.Parcel.writeBundle(Parcel.java:997)
at android.content.Intent.writeToParcel(Intent.java:10495)
at android.app.IActivityManager$Stub$Proxy.startService(IActivityManager.java:5153)
at android.app.ContextImpl.startServiceCommon(ContextImpl.java:1601)
at android.app.ContextImpl.startService(ContextImpl.java:1571)
at android.content.ContextWrapper.startService(ContextWrapper.java:669)
at android.content.ContextWrapper.startService(ContextWrapper.java:669)
看起来并不是binder不允许传递FD。下面分析相关源码,尝试寻找原因和突破点。先从抛出异常的代码开始。
/* http://aospxref.com/android-10.0.0_r47/xref/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_Binder.cpp#814 */
void signalExceptionForError(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, status_t err, bool canThrowRemoteException, int parcelSize) {
switch (err) {
//...
case FDS_NOT_ALLOWED:
jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException", "Not allowed to write file descriptors here");
break;
//...
}
}
/* http://aospxref.com/android-10.0.0_r47/xref/frameworks/native/libs/binder/Parcel.cpp#553 */
status_t Parcel::appendFrom(const Parcel *parcel, size_t offset, size_t len) {
//...
if (!mAllowFds) {
err = FDS_NOT_ALLOWED;
}
//...
return err;
}
看得出跟属性mAllowFds的设置有关。设置mAllowFds的代码在:
/* http://aospxref.com/android-10.0.0_r47/xref/frameworks/native/libs/binder/Parcel.cpp#575 */
bool Parcel::pushAllowFds(bool allowFds) {
const bool origValue = mAllowFds;
if (!allowFds) {
mAllowFds = false;
}
return origValue;
}
/* http://aospxref.com/android-10.0.0_r47/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Bundle.java#1250 */
public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) {
final boolean oldAllowFds = parcel.pushAllowFds((mFlags & FLAG_ALLOW_FDS) != 0);
try {
super.writeToParcelInner(parcel, flags);
} finally {
parcel.restoreAllowFds(oldAllowFds);
}
}
跟踪标志位FLAG_ALLOW_FDS的设置:
/* http://aospxref.com/android-10.0.0_r47/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Bundle.java#204 */
public boolean setAllowFds(boolean allowFds) {
final boolean orig = (mFlags & FLAG_ALLOW_FDS) != 0;
if (allowFds) {
mFlags |= FLAG_ALLOW_FDS;
} else {
mFlags &= ~FLAG_ALLOW_FDS;
}
return orig;
}
Bundle#setAllowFds(false)在多处代码有调用,如:Intent#prepareToLeaveProcess、LoadedApk$ReceiverDispatcher#performReceive、BroadcastReceiver$PendingResult#sendFinished、等,其中Intent#prepareToLeaveProcess被Instrumentation#execStartActivity调用。
上面涉及的代码都属于非公开接口,应用程序不应该调用。由此可知Android不希望在四大组件调用过程中传递FD,故意设置了门槛。
通过Bundle#putBinder突破Intent和四大组件的限制
已知通过aidl可以传递FD,且Bundle类有putBinder方法可以传递IBinder,那么不妨发一个IBinder到目标进程,然后用这个IBinder传递FD。虽然本质上还是aidl的调用,但可以不用依赖bindService等方法建立连接,而是通过Intent直接发到目标进程。
首先定义aidl:
interface IFileBinder {
ParcelFileDescriptor openFileDescriptor(int mode);
}
实现IFileBinder:
public class FileBinder extends IFileBinder.Stub {
final File mFile;
public FileBinder(File file) {
mFile = file;
}
@Override
public ParcelFileDescriptor openFileDescriptor(int mode) throws RemoteException {
try {
return ParcelFileDescriptor.open(mFile, mode);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RemoteException(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
发送FD:
File file = ...;
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putBinder("file", new FileBinder(file).asBinder());
Intent intent = new Intent(/*...*/);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
startActivity(intent);
接收FD:
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
IBinder binder = bundle.getBinder("file");
IFileBinder fileBinder = IFileBinder.Stub.asInterface(binder);
ParcelFileDescriptor fd = fileBinder.openFileDescriptor(ParcelFileDescriptor.MODE_READ_ONLY);
//...
通过IPC发送FD的结论
上面例举了若干跨进程传递FD的方法,相互各有优劣。如要从上述各方法中做选择,可以至少从以下几点来考虑:
- 源应用是否需要定制;
- 目标应用是否需要定制;
- 目标应用是否需要对FD做细粒度的控制;
- 源应用是否需要对目标应用做权限校验和控制;
- 代码的易维护性和易扩展性;
综合来说,FileProvider在各方面都是比较完备和可靠的文件共享机制。